Dive Brief:
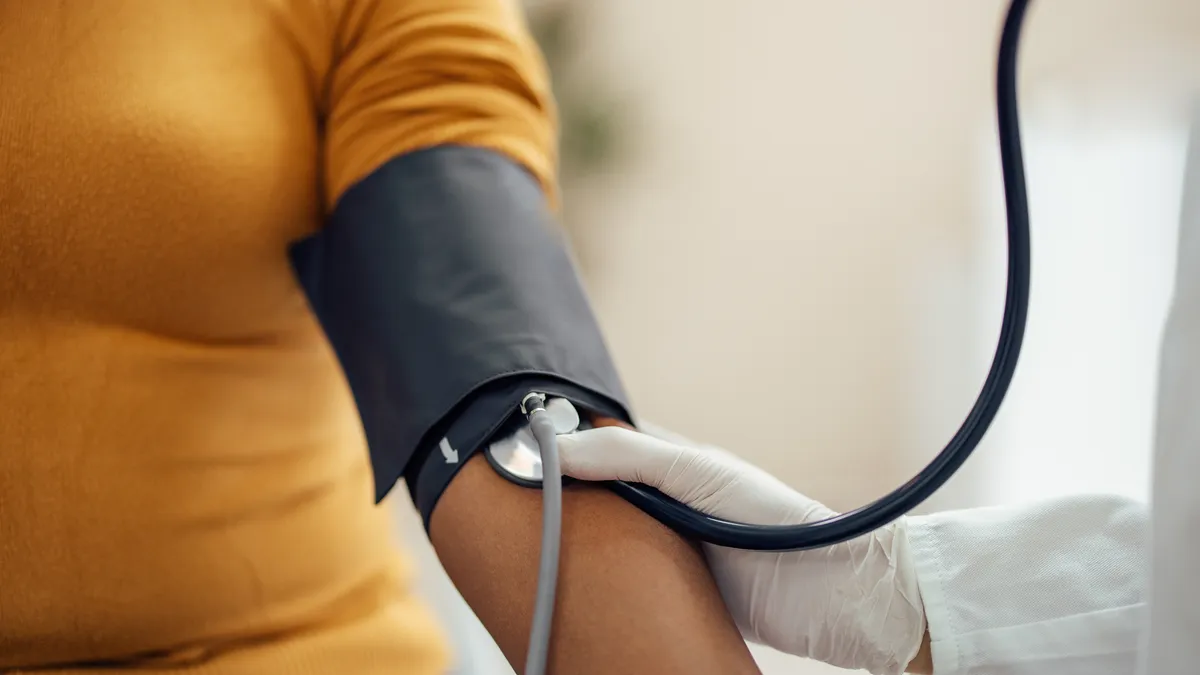
- An unmodified smartphone camera has detected 79% of cases of abnormally low blood oxygen levels in a six-subject study.
- The research, details of which were published in the journal npj Digital Medicine, expands on earlier smartphone-based oximetry projects by studying blood-oxygen saturation levels of as low as 70%.
- One of the six subjects, who identified as African-American, had a dark skin tone but the dataset is too limited for the researchers to conclude if the device suffers from the accuracy problems of standalone pulse oximeters.
Dive Insight:
Multiple research groups have sought to use smartphone cameras for pulse oximetry, either by adding hardware such as a color filter or by using software to process the signal. However, the authors of the npj Digital Medicine article found the earlier efforts had only tested saturation levels down to 80%, whereas the Food and Drug Administration requires developers to validate their oximeters from 70% to 100%.
To evaluate their software-based approach, the researchers enrolled six subjects to wear gas masks that delivered a controlled mix of oxygen and nitrogen to slowly lower their oxygen saturation. The subjects put one finger over a smartphone camera and another in a conventional pulse oximeter.
The design allowed the researchers to compare the results generated by the smartphone and standalone device over a wider range of saturation levels than other studies. Using a deep learning model, the team found the smartphone detected cases of sub-90% saturation with 81% sensitivity and 79% specificity. At sea level, blood oxygen levels are 96% to 98% in healthy individuals.
An accurate smartphone-based oximeter could support the low-cost clinical management of people with chronic and acute respiratory conditions, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and COVID-19. However, more work needs to be done before the technology tested in the study is ready for use. One issue is that smartphone cameras have different sensor configurations that may deliver variable results.