Dive Brief:
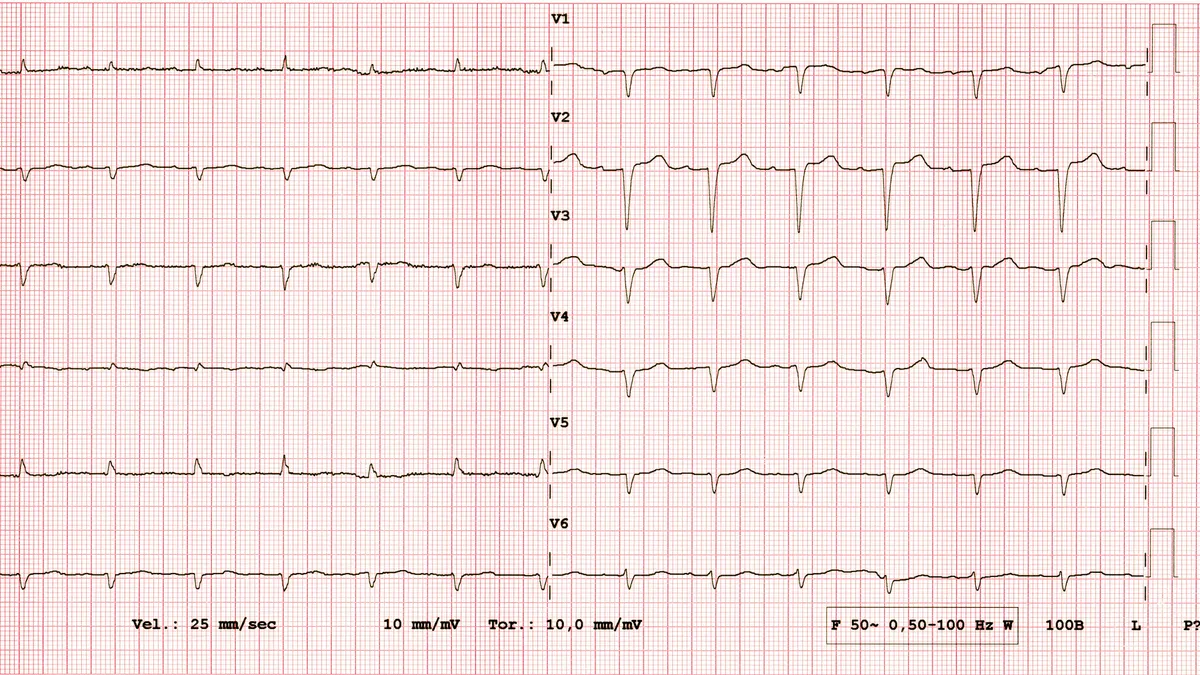
- Anumana, a health technology startup spun out of Mayo Clinic, entered a multi-year agreement with Pfizer to develop an algorithm to detect cardiac amyloidosis, a serious heart condition.
- Cardiac amyloidosis is characterized by a buildup of protein deposits in the heart muscle, causing it to become thick and stiffened, and affecting the left ventricle’s ability to fill with blood and pump blood out of the heart. While it can lead to heart failure, early treatment can stop the damage.
- Anumana plans to conduct a clinical trial validating the algorithm and seek de novo clearance in the U.S. It also will seek regulatory approval in Europe and Japan.
Dive Insight:
Anumana and Pfizer struck a research agreement, which would support the development of an algorithm using electrocardiogram (ECG) data to identify patients who may be at risk of a rare disease called cardiac amyloidosis. Although the condition can be difficult to diagnose because symptoms can vary and seem unrelated, the companies hope to detect it earlier using ECGs, which are widely available.
“The challenge in diagnosing cardiac amyloidosis can prevent patients from getting treatment while the disease continues to progress,” Anumana Chief Business Officer David McMullin said in a statement. “We believe this collaboration will demonstrate the power of Anumana’s AI-ECG algorithms to help clinicians intervene earlier, giving them greater ability to improve patient outcomes and prolong lives.”
Cambridge, Mass.-based Anumana was founded in 2021 through a partnership between Mayo Clinic and health technology company nference, with the plan of developing and commercializing AI-enabled health algorithms. To start, the company has focused on detecting heart conditions using ECG data and currently has breakthrough device designation for algorithms to detect low ejection fraction, pulmonary hypertension and hyperkalemia.